 Prior to 2019 planting, AgVenture published an update on the advancement of tar spot across the Midwest. As of last week, AgVenture Corn Product Manager Darren Bakken has seen the disease move as far west as Boone County, Iowa. University research shows that the disease has spread across much of the state of Iowa as of October 10, 2019 (see map).
Prior to 2019 planting, AgVenture published an update on the advancement of tar spot across the Midwest. As of last week, AgVenture Corn Product Manager Darren Bakken has seen the disease move as far west as Boone County, Iowa. University research shows that the disease has spread across much of the state of Iowa as of October 10, 2019 (see map).
Pathologists at Iowa State University have been studying and mapping the disease, caused by the fungus Phyllachora maydis, throughout the 2019 growing season in Iowa. They have observed tar spot in 75 of Iowa’s 99 counties and scouting for the disease has started in northeast Nebraska counties. While the disease has not appeared severe in most cases in Iowa this year, there is concern for how quickly it spread west. Now that the pathogen is present in the state, tar spot will continue to be a problem in 2020 and beyond.
Tar spot produces small, raised stromata (spots) on the upper and lower leaf surface. Stromata can occur singularly or in clusters and fisheye legions (tan or brown lesions around the tar spots) have also been reported in certain cases. Tar spot can be confused with southern or common rust, so please refer to your AgVenture Yield Specialist to assist in diagnosing your corn plants.
If tar spot is present on your farm, rotating fields out of corn may help reduce the inoculum in the field. A fungicide application may also be beneficial, depending on when the disease is observed and the timing of the application.
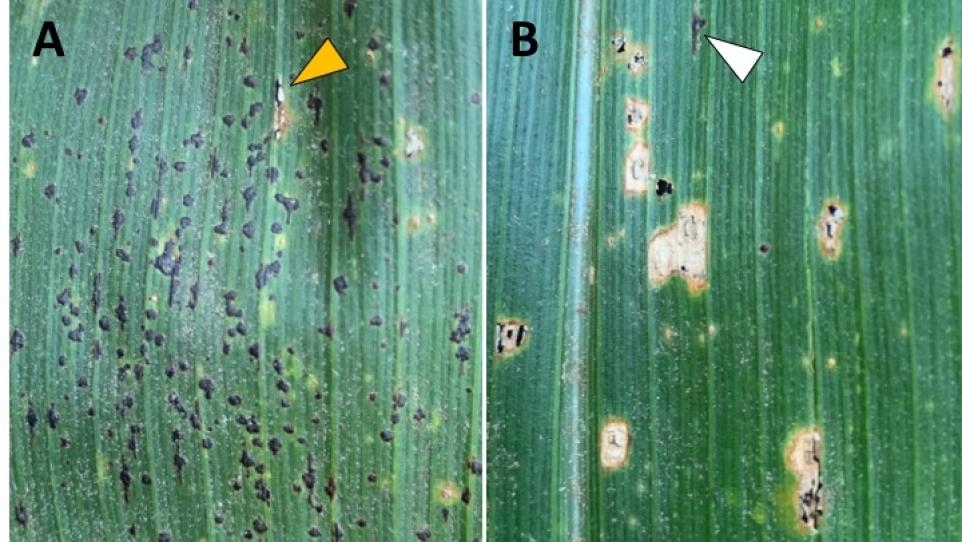 Comparison between tar spot stromata (A) and rust pustules producing black teliospores (B). The orange arrow in A points to a rust pustule among tar spot stromata; the white arrow in B points to a tar spot stroma among rust pustules. (Photo credit: Iowa State University).
Comparison between tar spot stromata (A) and rust pustules producing black teliospores (B). The orange arrow in A points to a rust pustule among tar spot stromata; the white arrow in B points to a tar spot stroma among rust pustules. (Photo credit: Iowa State University).
For further information on tar spot, please refer to the following site: https://corn.ipmpipe.org/tarspot/ or download a PDF from the Crop Protection Network https://crop-protection-network.s3.amazonaws.com/publications/tar-spot-filename-2019-03-25-120313.pdf.